Projects
Rethinking the mini-map: A navigational aid to support spatial learning in urban game environments
Overview
- Examined the impact of game navigation aids on spatial knowledge development.
Study Approach
- Conducted randomized study comparing landmark-based verbal directions vs. mini-maps.
Key Insights
- Verbal directions outperformed mini-maps in enhancing spatial knowledge.
- Mini-maps demonstrated higher navigational efficiency.
Implications
- Suggested a need to balance navigational efficiency and spatial learning in virtual environments.
- Our study investigates the impact of game navigation aids on spatial knowledge development in virtual environments.
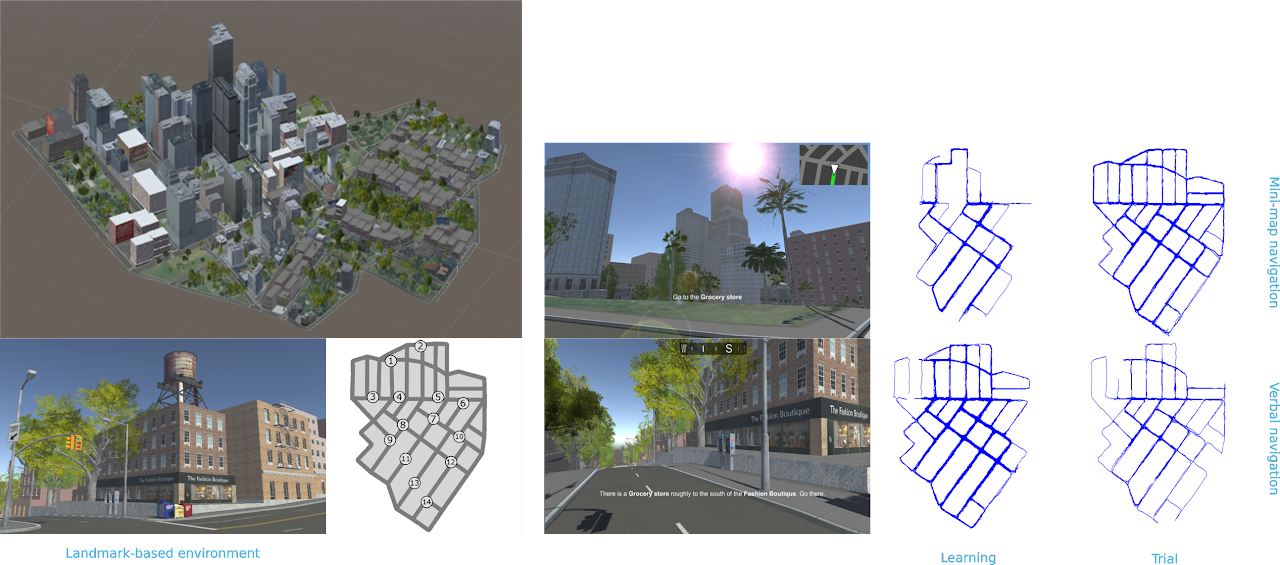 |
|---|
| (left) the 3D urban environment; a survey view of the 3D environment with landmarks; (middle) navigational aids as mini-map and verbal instructions; (right) participants’ traversal patterns during learning and trial tasks. |
Leveraging fog computing for sustainable smart farming using distributed simulation
Overview
- Developed a simulation framework catering to sensor deployment and data processing in smart farming.
Framework Features
- Facilitated simulation of diverse farming scenarios.
- Supported sensor placement, coverage area, and line of sight deployment.
- Modeled data gathering via relay mechanisms or airborne systems.
- Included mobility and energy models for sensors and airborne vehicles.
- Incorporated fog computing for backend computing support.
Contribution
- Addressed the gap in existing literature by considering network parameters.
- Benchmarked system performance metrics like transmission delay and energy consumption.
Implications
- Offered a comprehensive framework for understanding sensor deployment and data processing in smart farming practices.
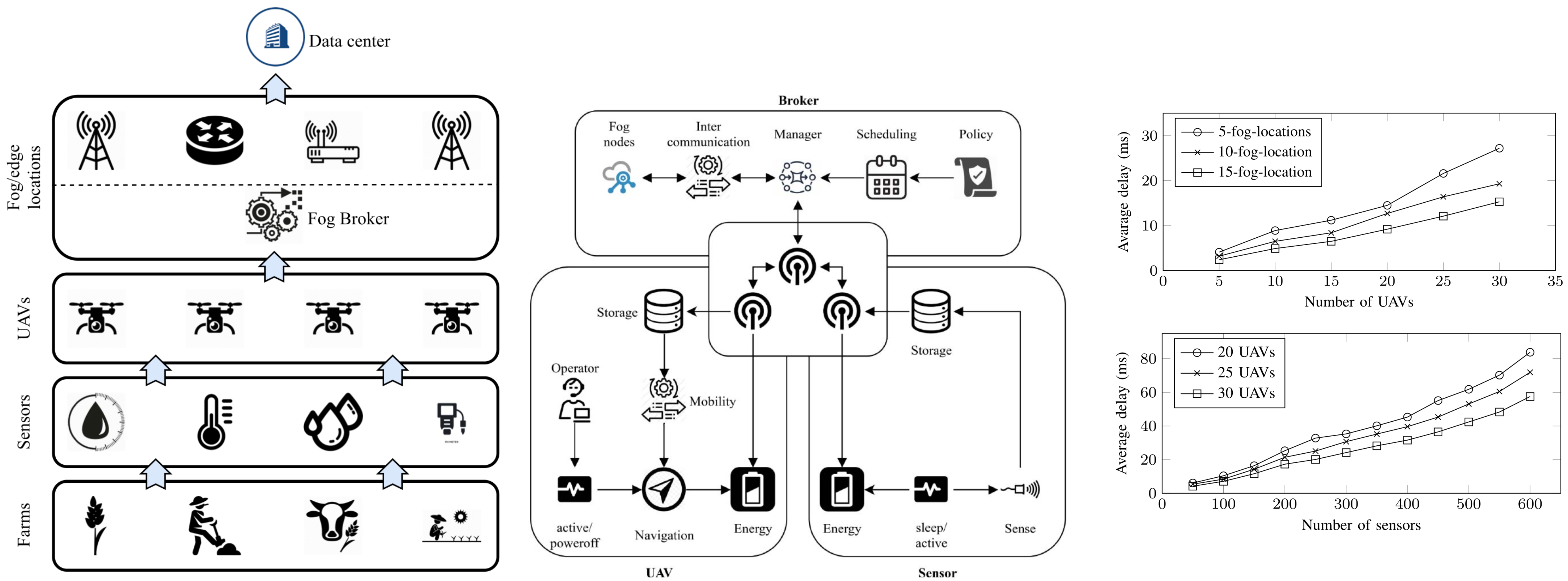 |
|---|
| Smart farming toolkit layered architecture. |
Internal architecture of the proposed framework.
Average delay between UAVs and fog nodes when varying the number of available fog locations.
Delay between sensors and UAVs when varying the number of deployed UAVs.
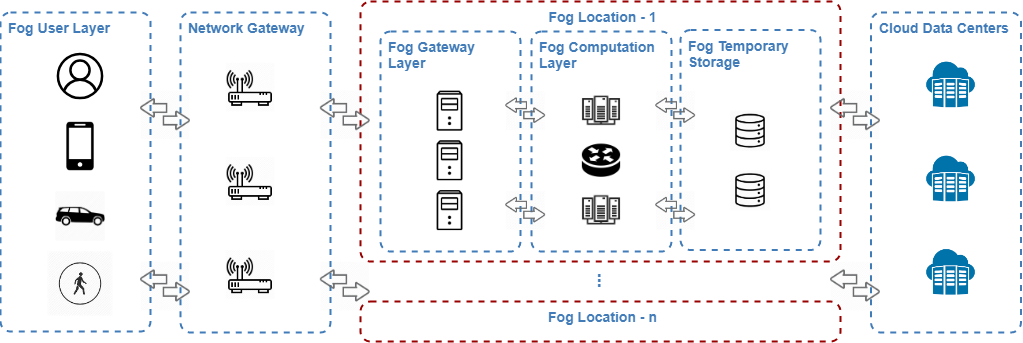
xFogSim: A Distributed Resource Management Framework for IoT Services in Fog Federation
Overview
- Developed xFogSim, a framework optimizing fog resource allocation for latency-sensitive IoT applications.
Framework Capabilities
- Focused on reducing network congestion by leveraging fog computing.
- Addressed limitations of existing fog-based simulators.
- Introduced key features: network delay, latency, and packet error rate management.
- Integrated multi-objective optimization for cost, availability, and performance.
- Implemented locality-aware distributed broker node management.
Contributions
- Filled gaps in fog-based simulators by incorporating crucial network parameters.
- Introduced an optimized fog framework for latency-sensitive applications.
Implications
- Offered a lightweight, configurable solution for managing dynamic resource provisioning across fog nodes, ensuring efficient handling of numerous user requests.
 |
|---|
| abc. |
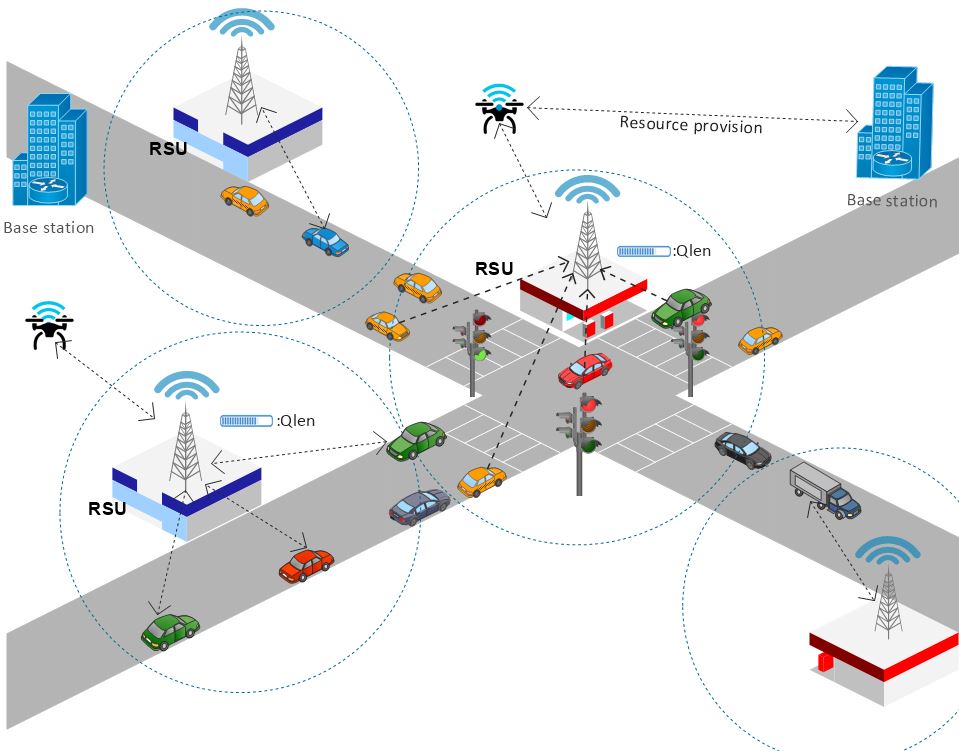
On-demand resource provisioning for vehicular networks using flying fog
Overview
- Developed a framework leveraging flying fog units to optimize resource allocation for delay-sensitive applications in smart cities.
Framework Focus
- Addressed latency issues by deploying computing devices at edge locations.
- Introduced a preemptive resource provisioning model for effective resource allocation.
Key Features
- Incorporated flying fog units to alleviate congestion in overloaded edge locations.
- Defined lease periods for allocated resources based on preemptive provisioning.
Contributions
- Offered a solution for managing computing requests in congested environments.
- Improved system efficiency by reducing wait times and enhancing overall performance.
Implications
- Demonstrated a 9% reduction in wait times and a corresponding 9% increase in system efficiency compared to baseline approaches, showcasing the effectiveness of the framework in optimizing resource allocation for delay-sensitive applications in smart city environments.
 |
|---|
| abc. |
CrowdFix: An eyetracking dataset and visual saliency model for crowded videos
Overview
- Developed CrowdFix, a comprehensive database containing crowd videos and eye-tracking data for in-depth analysis of crowd behavior.
Database Content
- Comprised 434 diverse crowd videos across three categories: Sparse, Dense Free Flowing, and Dense Congested, totaling 37,493 frames and 1,249 seconds.
- Videos are in 720p resolution at a 30 Hz frame rate.
Eye-Tracking Experiment
- Utilized the EyeTribe eye tracker for eye movement monitoring in an experiment involving 26 non-expert participants (10 males, 16 females) aged 17 to 40.
- Participants had normal or corrected-to-normal vision, maintained a fixed distance of 60 cm from the monitor, and underwent a 9-point calibration process.
Experimental Procedure
- Subjects performed free-viewing tasks of videos presented MTV style after calibration.
- Collected fixations from all 32 subjects across 538 videos, contributing to the eye-tracking database.
Contributions
- Created a comprehensive database coupling crowd videos with eye-tracking data for studying crowd behavior and eye movement patterns, catering to research in crowd scene analysis and saliency modeling.
 |
|---|
| abc. |
Sustainable vehicle-assisted edge computing for big data migration in smart cities
Framework Description
- Proposed an innovative large-scale data migration framework leveraging vehicles as data carriers within smart city environments.
Data Migration Process
- Utilized a neural network to identify suitable vehicles as data mules, selecting those heading toward the data destination.
- Facilitated reduced backend network usage, optimizing bandwidth and decreasing overall energy consumption.
Comparative Analysis
- Evaluated the proposed framework against traditional internet data transfer methods and a non-machine intelligence approach.
Results and Findings
- Achieved a 67% success rate with data transfers 193 times faster than the average internet bandwidth (21.28 Mbps).
- Reduced CO2 emissions significantly; for 30 TB data transfers, emissions were 6.403 kg, substantially lower compared to 1172.8 kg for standard internet usage.
Contribution
- Developed a novel data migration paradigm utilizing neural network intelligence and vehicle mobility, significantly improving data transfer efficiency, minimizing energy consumption, and reducing environmental impact within smart city infrastructures.
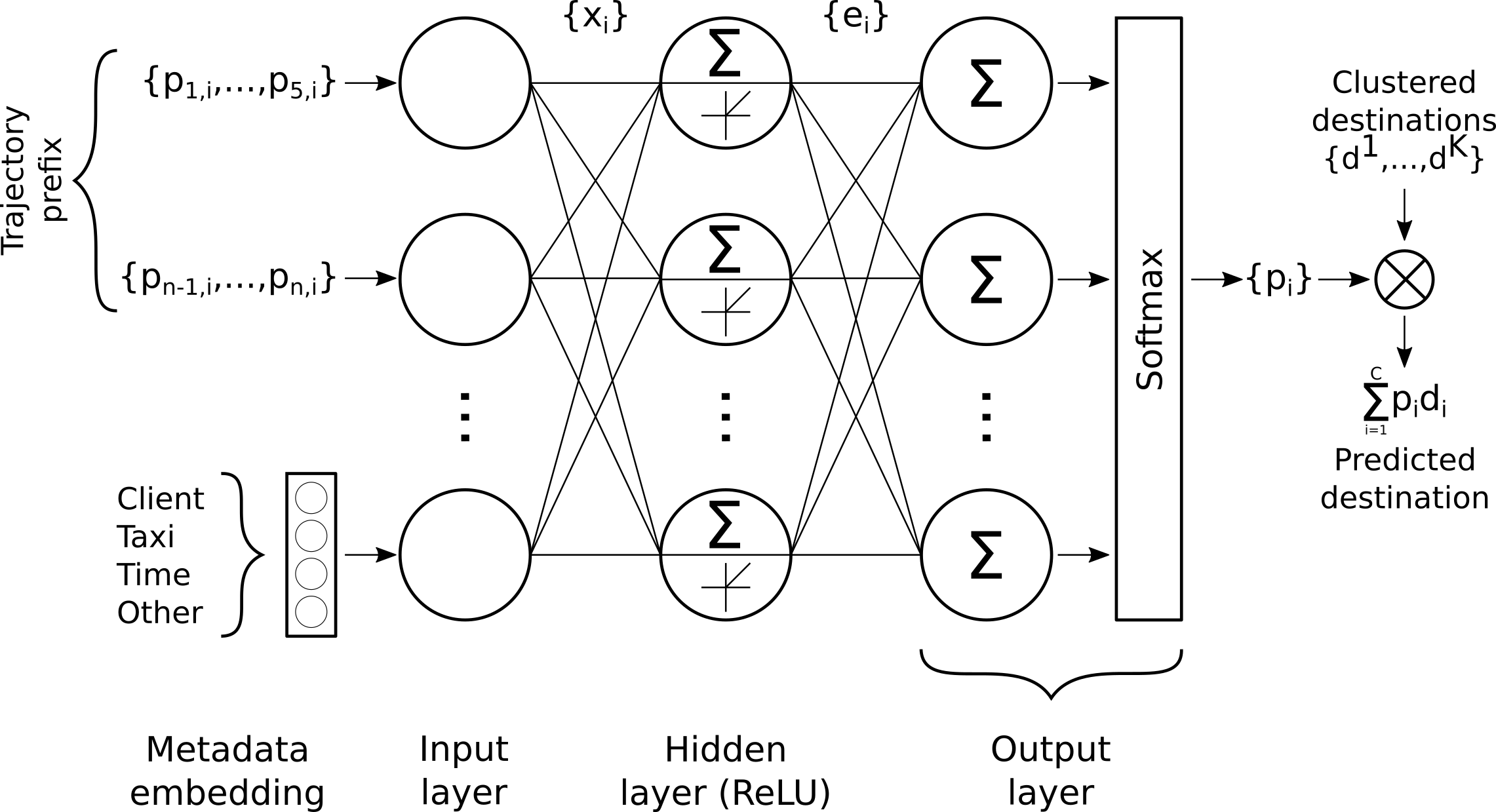 |
|---|
| abc. |
Unsupervised video object segmentation using conditional random fields
Segmentation Technique
- Introduced an innovative graph-based superpixel segmentation approach, facilitating spatiotemporal oversegmentation of videos.
Methodology
- Developed a threshold-based foreground separation model applied to the generated superpixels.
- Utilized a conditional random field along with an energy minimization technique to define and solve a potential function, resulting in precise video segmentation.
- Experimental Validation
- Conducted comprehensive experiments on two diverse datasets comprising over 24 videos.
- Demonstrated superior or competitive performance compared to state-of-the-art algorithms in video object segmentation.
Contribution
- Proposed a novel segmentation technique combining graph-based superpixels and conditional random fields, offering improved accuracy and efficacy in video object segmentation, as validated across diverse datasets.
 |
|---|
| abc. |
A framework to combine multi-object video segmentation and tracking
Approach Overview
- Leveraged the synergies between multi-object video segmentation and tracking to enhance accuracy in identifying and maintaining object identities across video frames.
Methodology
- Implemented independent modules for multi-object tracking and segmentation on a dedicated dataset.
- Multi-object tracking employed higher-order smoothness constraints via Lagrangian relaxation to iteratively refine object trajectories.
- Segmentation employed clustering to create superpixels, trained a linear SVM using Lab color for foreground-background segmentation, and utilized color and optical flow for ID labeling.
- Conducted joint processing:
- Refinement of tracking bounding boxes based on segmentation results for precise target localization.
- Improved ID labeling by leveraging the tracking module’s accuracy to correct segmentation errors.
- Reciprocally added target detections missed initially by either module based on the results of the counterpart module.
Validation
- Demonstrated significant improvements in both tracking and segmentation accuracy through joint processing, as evidenced by comprehensive experimental results.
- Achieved performance levels comparable to state-of-the-art techniques in both segmentation and tracking within video datasets.
 |
|---|
| abc. |
Three pathway spatiotemporal visual saliency model
Project Overview
- Developed a sophisticated visual saliency model by incorporating face detection, dynamic motion, and static visual features to predict eye movements during free video viewing.
Methodology
- Designed a multi-faceted saliency model:
- ‘Static’ saliency emphasized contextual differences in luminance, orientation, and spatial frequency.
- ‘Dynamic’ saliency highlighted moving regions proportionate to motion amplitude.
- ‘Face’ saliency identified and prioritized areas with detected faces, weighted by detection confidence.
- Conducted a behavioral experiment to record participants’ eye movements while watching videos.
- Quantified the efficiency of the saliency model by comparing the recorded eye movements with the generated saliency maps.
- Addressed center bias influence on saliency maps and incorporated this bias effectively into the model.
- Proposed an efficient fusion method amalgamating all saliency maps into a unified master saliency map.
- Designed a multi-faceted saliency model:
Outcomes
- The fused master saliency map emerged as a robust predictor of participants’ eye positions during video viewing, showcasing the model’s efficacy in foreseeing human eye movements.
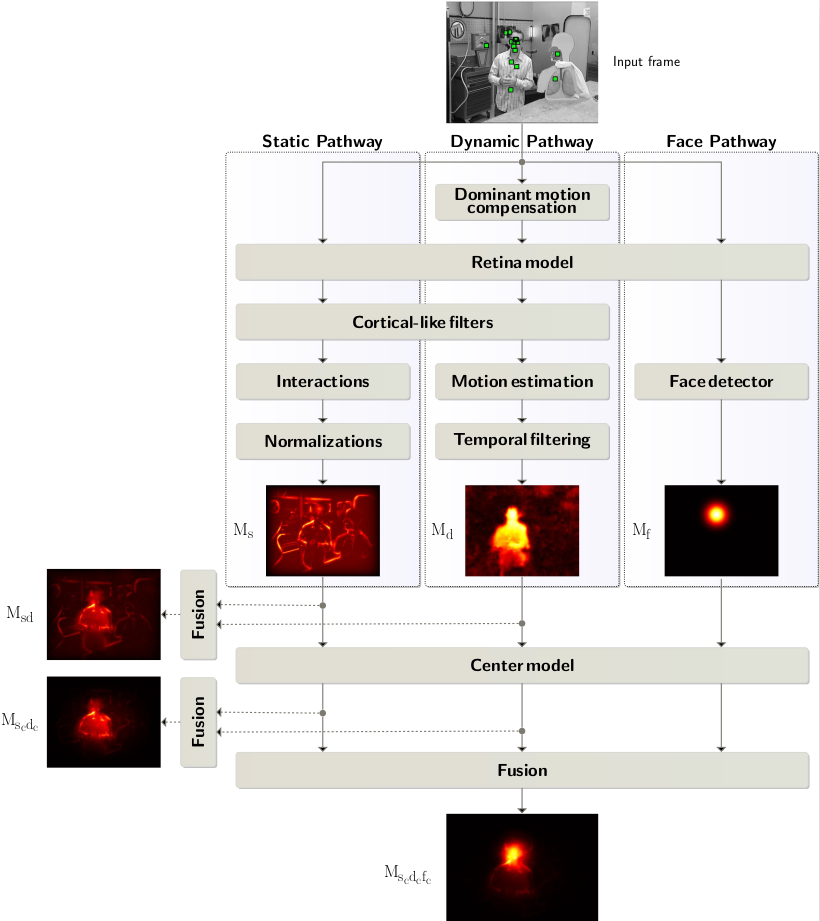 |
|---|
| abc. |
 |  |
|---|---|
| abc. | abc. |
Parallel implementation of a spatio-temporal visual saliency model
- Project Summary
- Explored computer vision models, particularly focusing on visual saliency, crucial for diverse applications such as robotics, image analysis, compression, and video indexing. Addressed computational intensity and real-time constraints associated with existing models.
Methodology
- Selected a spatiotemporal model merging static and dynamic information, deemed suitable for various applications.
- Engineered a highly efficient implementation of the selected model, utilizing multi-GPU architecture to achieve real-time processing.
- Outlined the algorithms of the model and presented parallel optimizations executed on GPU to enhance precision and execution time.
- Outcomes
- Realized a breakthrough in computational efficiency, achieving real-time execution of the multi-path model on multi-GPU systems.
- This highly efficient implementation serves as a robust tool, streamlining various vision-related applications by providing faster and precise visual saliency analysis.
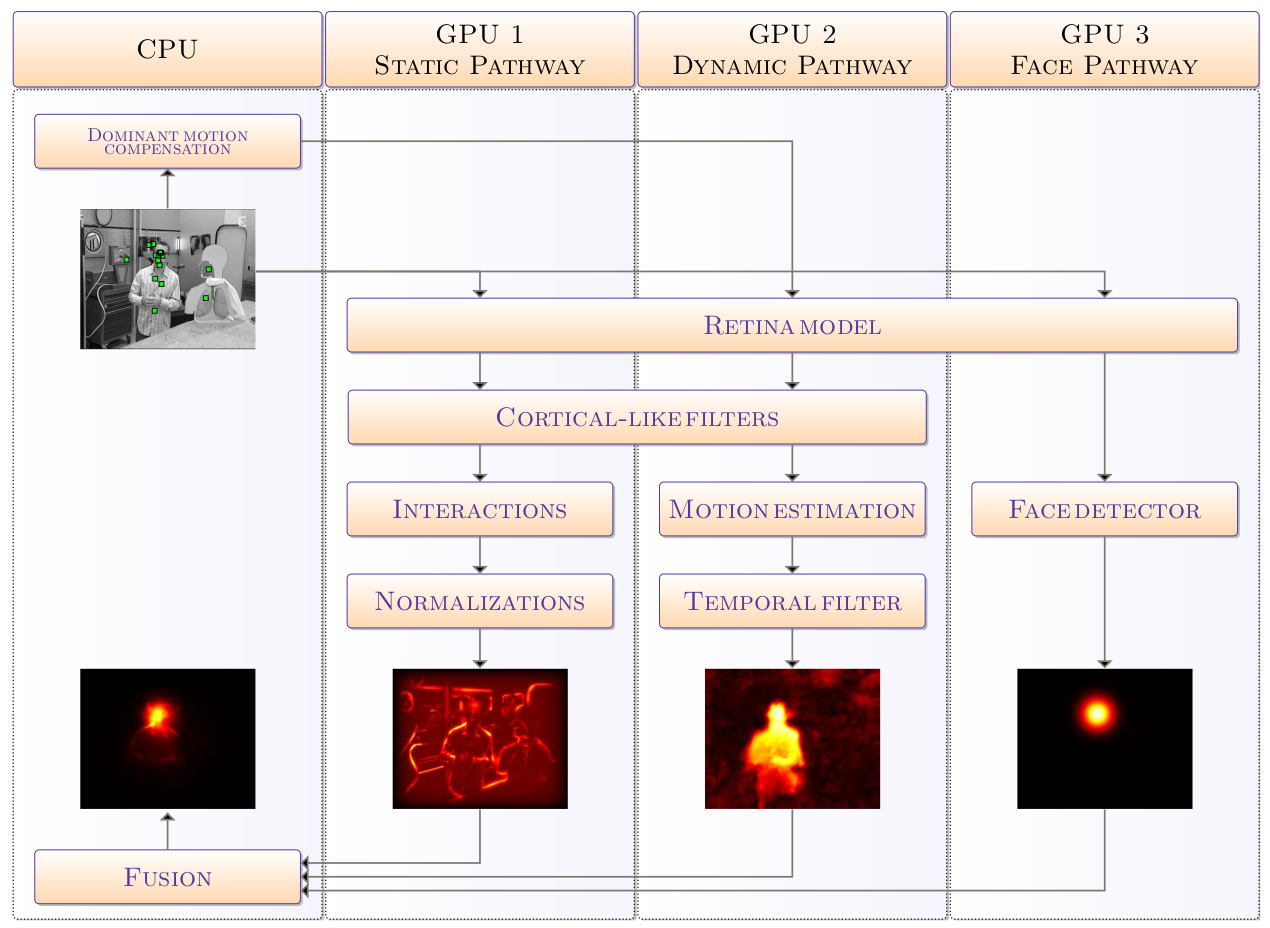 |
|---|
| abc. |
Exploiting class hierarchies for large-scale scene classification using hybrid discriminative approach
Project Summary
- Explored challenges in scene classification due to image variability, ambiguity, and diverse conditions. Developed a novel approach leveraging fine-to-coarse category mappings and feature fusion to address these challenges, enhancing the accuracy of scene classification models.
Methodology
- Established a baseline model using traditional bag-of-words methodology for comprehensive evaluation.
- Proposed a novel model based on fine-to-coarse category mappings, integrating information from feature descriptors to create a unified feature representation.
Outcomes
- Demonstrated significant performance improvement compared to baseline and contemporary methods.
- Validated the effectiveness of the proposed model through diverse evaluation metrics.
- Achieved a well-balanced framework, optimizing the trade-off between computational efficiency and model accuracy in scene classification.
 |
|---|
| abc. |
Large-scale image geo-tagging using affective classification
Project Summary
- Explored emotional aspects in machine learning and decision-making, particularly in image processing for Geo-tagging. Proposed a hybrid approach merging Elements-of-Art based emotional features (EAEF) and Principles-of-Art based emotional features (PAEF) for more accurate image classification.
Methodology
- Conducted experiments using EAEF and PAEF separately to analyze their effectiveness in image emotional classification.
- Formulated a Hybrid feature vector by combining EAEF and PAEF, conducting experiments to assess its performance.
Outcomes
- Demonstrated superior accuracy with the hybrid approach compared to individual methods.
- Utilized Yahoo Flickr Creative Commons 100 Million (YFCC100M) dataset, containing geotagged images, for research and experimentation.
- Applied the emotional intelligence aspect of machine learning in Geo-tagging, showing potential implications in various domains like E-Health and E-Learning.
 |
|---|
| abc. |
